Simple diffusion- Definition, principle, examples, applications

Simple diffusion is a type of passive transport which, as the name suggests, is simply the movement of solute which occurs when its electrochemical potentials on the two sides of a permeable barrier are different.
- While in other science disciplines like chemistry, diffusion refers to “spreading out” of molecules from a higher concentration in biology, the process involves a selectively permeable biological membrane.
- In simple diffusion, like all other passive transport mechanisms, the movement of molecules occurs along the concentration gradient until the concentration of solute is uniform on either side.
Principle of Simple diffusion
How does simple diffusion work?
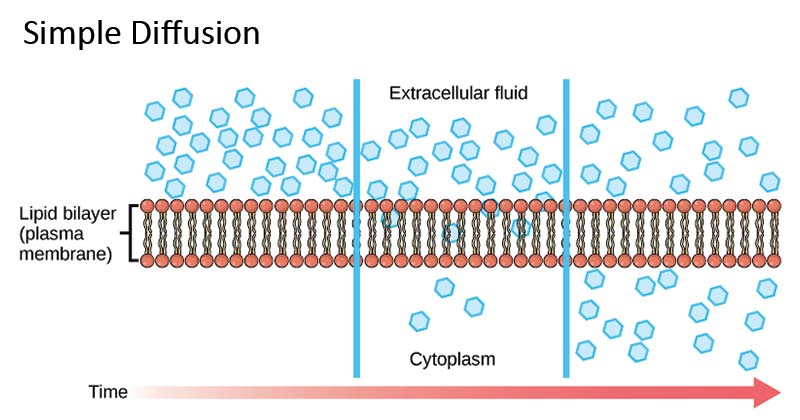
- In free diffusion through a membrane, the solute particles move about by random Brownian motion, like that in free solution.
- The solute flux, which is a measurable and reproducible quantity, is essentially the result of these separate motions.
- Even though the path of a single solute particle cannot be predicted, the sum of an enormous number of these paths is quite reproducible.
- The flux in free diffusion can be written very simply, in a form proposed by Teorell (1953):
Flux = Mobility * Concentration * Driving Force
- The flux is the number of moles of solute crossing one square centimeter of membrane per second.
- The flux is proportional to the product of the solute mobility, which measures the ease of transport, the concentration, which measures the amount of material available to participate in the process, and the driving force.
- When the chemical potential of the solute is the same in the two phases bounding the membrane, the solute is in equilibrium, and its flux across the membrane is zero.
- However, when the concentration is different, a chemical gradient potential is developed, which is the driving force for the flux of solute.
- The mobility of the solute, in turn, depends on the permeability of the membrane for that particular solute and for biological systems, the permeability must be found experimentally.
Diffusion of electrolytes
- The principle for the diffusion of charged species is driven by an additional force along with the concentration gradient.
- Charged solutes are subject to electrical forces when electrostatic potential gradients are present.
- Accordingly, the driving force for electrolyte transport is the gradient of the electrochemical potential rather than that of the chemical potential.
- Since any electrolyte solution must contain at least one anion and one cation, there are always at least two solute species which results in multiple fluxes.
Factors affecting Simple diffusion
Because the rate of diffusion is determined by several parameters, these parameters/factors affect the mechanism of diffusion.
- Concentration gradient
- The concentration gradient across a biological membrane is the driving force for the diffusion of a nonelectrolyte.
- Therefore, the higher the concentration difference across the membrane, the higher will be the rate of diffusion.
- As the distribution of molecules across the membrane moves towards uniformity, the rate of diffusion decreases.
- Once equilibrium is maintained across the membrane, the process of diffusion ceases.
- Mass/Size of the solute molecules
- The size of the molecules also affects the rate of diffusion across a biological membrane.
- If the size of the molecules is large, it will be more difficult for it to move across the membrane, which, in turn, slows the rate of diffusion of the molecule.
- Thus, the rate of diffusion is higher for smaller molecules and slower for larger molecules.
- Temperature
- The temperature of the system also affects the process of simple diffusion.
- With the increase in temperature, the energy of the molecules also increases.
- Molecules with higher energy can move faster across the membrane while particles with lower energy move slower.
- Solubility
- The solubility of molecules in a medium also affects the rate of diffusion of the particles.
- Molecules which are lipid-soluble can move quickly across the lipid layer like the plasma membrane.
- Similarly, polar and non-polar molecules also move with a different rate depending on the nature of the biological membrane.
- Solvent density
- With the increase in solvent density, the rate of diffusion decreases.
- More dense a solvent, more difficult it will be for the solute to move around.
- Solvent density plays an essential role in the movement of solute in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- An increase in the density of the cytoplasm slows down the movement of the molecules and gases, and the reverse is true for less dense cytoplasm.
- Surface area and thickness of the biological membrane
- The rate of diffusion increase with the increase in the surface area of the membrane.
- The increase in surface area increases the permeability or mobility of the molecules as mobility is one of the factors responsible for the flux.
- Similarly, the rate of diffusion is also reduced by the increasing thickness of the membrane.
Examples of Simple diffusion
Oxygen and Carbon dioxide
- One of the classic examples of simple diffusion is the movement of gases across the membrane in animals.
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood is exchanged by the process of simple diffusion.
- Depending on the concentration gradient of these gases in the cells, the direction of the movement of gases is determined.
- In the alveoli, the concentration of oxygen is more as compared to the blood vessels under inhalation. Thus, the movement of oxygen occurs from alveoli to the blood.
- Similarly, during exhalation, the concentration of carbon dioxide is more in the blood as compared to the alveoli, which results in the movement of carbon dioxide towards the lungs.
- A similar process occurs during the exchange of gases between blood and cells.
Movement of waste materials
- In animals, the removal of waste materials occurs via simple diffusion.
- In the liver, waste material, urea, is excreted onto the blood by the process f simple diffusion.
- Similarly, in kidneys, removal of waste chemicals and toxins and absorption of water occurs via simple diffusion. A separate active transport also occurs in some parts of the kidneys.
Nutrition in bacteria
- Prokaryotes like bacteria do not have a specialized mechanism for the movement of nutrition, water, gases and other solutes throughout their body.
- Therefore, they rely on the process of simple diffusion for the movement of these molecules within the cytoplasm.
- In addition, the excretion of waste materials in bacteria is also aided by simple diffusion as it occurs via the general body surface.
Application of Simple diffusion
The concept of simple diffusion is applied in various fields like the food, medicine, and environment
- In beverages like tea and soda, the diffusion of gases and chemicals from tea leaves plays a vital role in the development of the particular taste.
- The process of simple diffusion is applied in the action of medicines in the body. Once a medicine is ingested, the molecules are released into the respective sites of action through the process of simple diffusion.
- Air pollution is another phenomenon that is a result of diffusion. The diffusion of various gases released from agricultural, industrial, and mechanical processes results in air pollution.
- The formation of alloys is also a result of diffusion. Under long-term exposure of one metal to another, the atoms diffuse from one metal to another to fill the spaces. This results in the formation of different alloys.
References
- Friedman, M. (2008). Principles and models of biological transport. Springer.
- https://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-diffusion.html
- https://biologydictionary.net/simple-diffusion/
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/Book%3A_General_Biology_(Boundless)/5%3A_Structure_and_Function_of_Plasma_Membranes/5.2%3A_Passive_Transport/5.2C%3A_Diffusion
Sources
About Author



